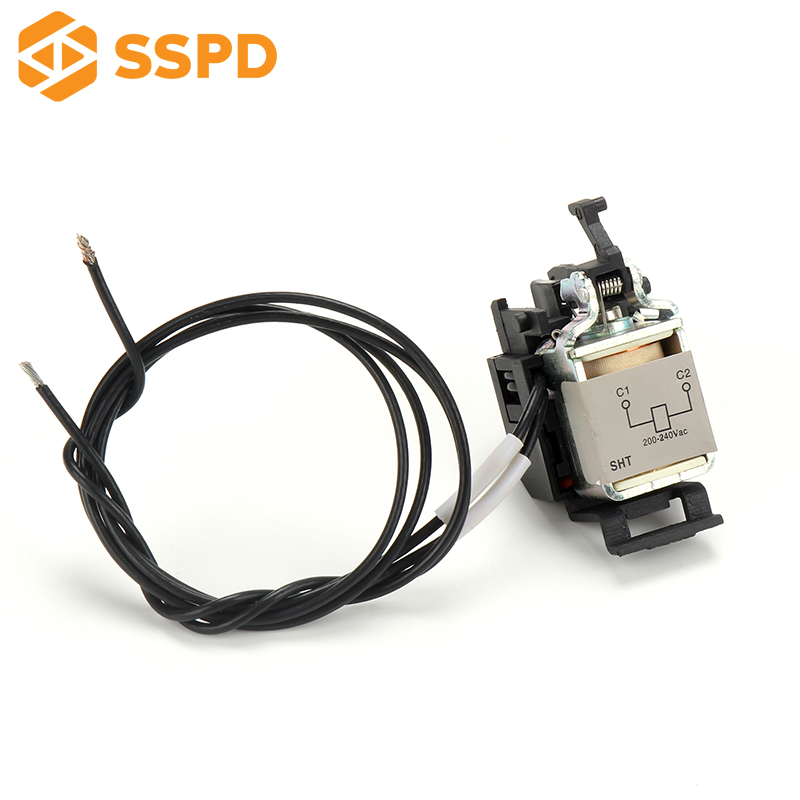
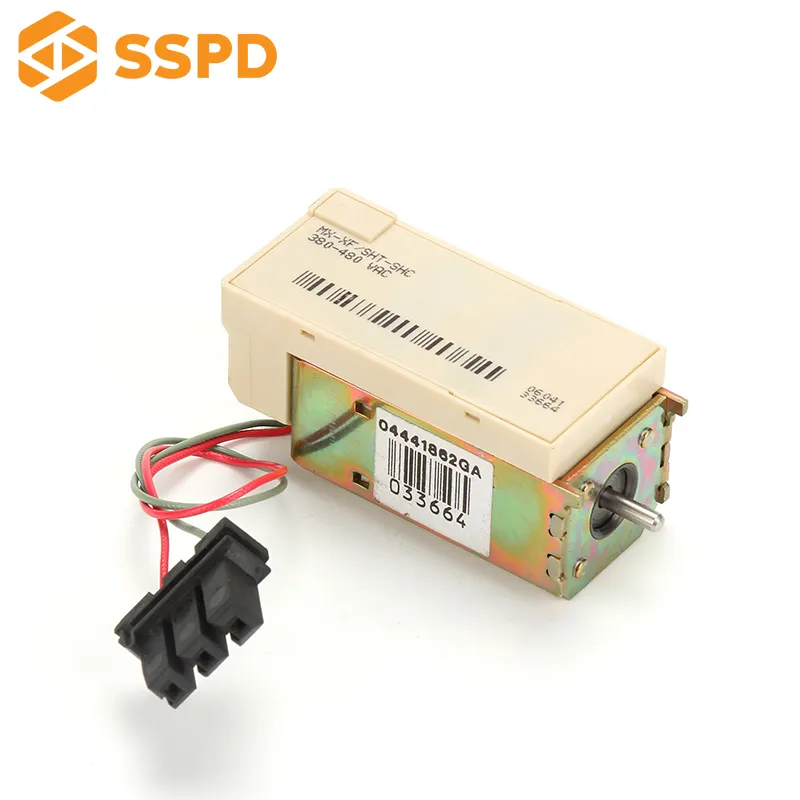
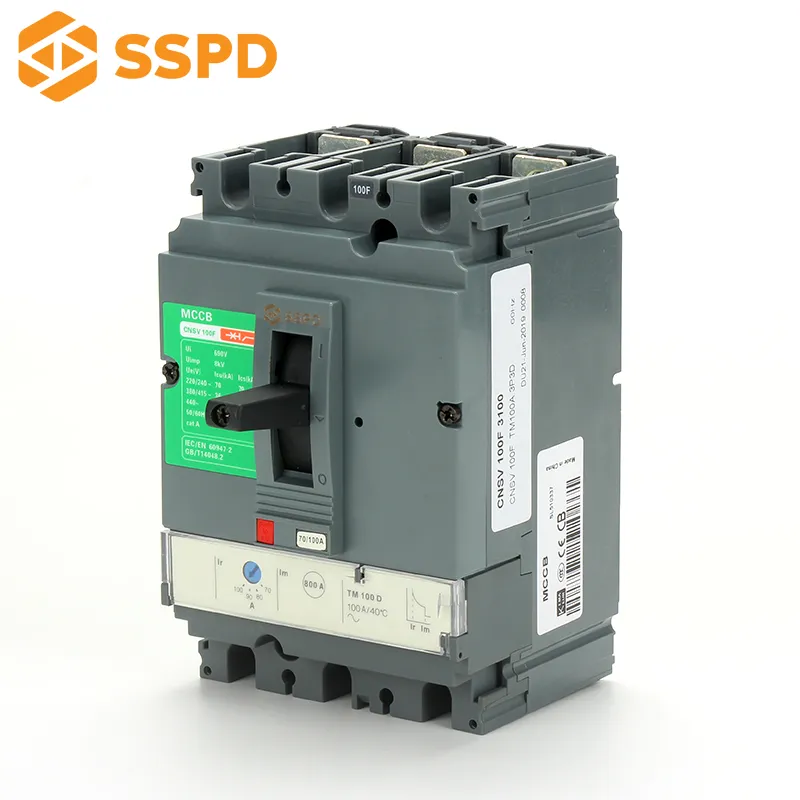
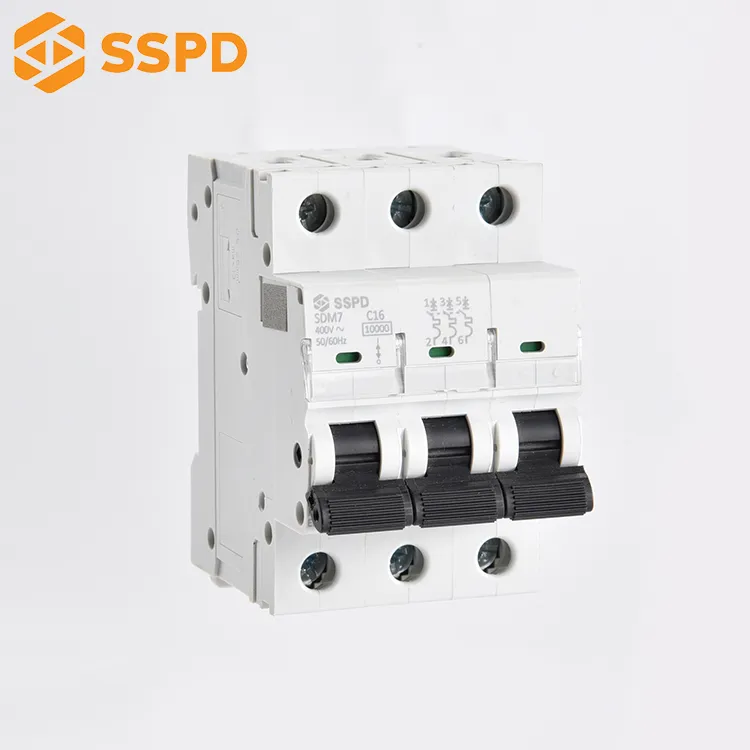
The trip unit is a device mechanically connected to the circuit breaker to release the holding mechanism and automatically disconnect the circuit breaker. Its function is that the vector sum of the current passing through the zero-sequence current transformer is not equal to zero when there is leakage in the line or personal electric shock, and the voltage is generated on both sides of the secondary coil of the transformer, and is amplified by the integrated circuit. The trip unit cuts off the power supply within 0.1 seconds, thus playing the role of electric shock and leakage protection.
Release function
The trip unit has protection functions such as overload, open circuit, leakage, undervoltage, overvoltage, unbalance, underfrequency, overfrequency, reverse power, phase sequence, etc. It also has load monitoring, real-time value measurement, demand measurement, and harmonic measurement. , Measurement table setting, maintenance, communication, DI/DO, regional selective interlocking, test interlocking, LCD interface display and other functions.

Classification of trip units
1. Thermal release
Thermal magnetic release provides magnetic protection and thermal protection, thermal protection is overload protection. Thermal protection: When the current passes through the release, the thermal element heats up (the direct heating current directly passes through the bimetallic sheet), and the bimetallic sheet is deformed by heat. When the deformation reaches a certain level, it hits the drawbar to drive the mechanism to cut off the circuit. Generally speaking, thermal magnetic trips are used in circuits to provide short-circuit and overload protection. Only in some special occasions, electromagnetic trips are used to provide short-circuit protection, while other components (such as thermal relays) provide overload protection.
2. Electromagnetic release
The electromagnetic release is connected in series with the protected circuit. When a normal current passes through the line, the electromagnetic force generated by the electromagnet is less than the pulling force of the reaction force spring, the armature cannot be attracted by the electromagnet, and the circuit breaker operates normally. When a short circuit fault occurs in the line, the current exceeds several times of the normal current, the electromagnetic force generated by the electromagnet is greater than the force of the reaction force spring, and the armature is attracted by the electromagnet and pushes the free tripping mechanism to release the main contact through the transmission mechanism. The main contacts separate and cut off the circuit under the action of the opening spring to protect the short circuit.
3. Loss of pressure release
The voltage-loss release is connected in parallel with the power supply side of the circuit breaker, which can play the role of under-voltage and zero-voltage protection. When the power supply voltage is normal, the operating handle is pulled, the normally open auxiliary contact of the circuit breaker is closed, the electromagnet is energized, the armature is attracted by the electromagnet, and the main contact can be locked in the closed position by the free trip mechanism, and the circuit breaker is put into operation. . When the power supply side is powered off or the power supply voltage is too low, the electromagnetic force generated by the electromagnet is not enough to overcome the pulling force of the reaction force spring, the armature is pulled up, and the free tripping mechanism is pushed by the transmission mechanism to make the circuit breaker trip, resulting in undervoltage. and zero voltage protection.
When the power supply voltage is 75% to 105% of the rated voltage, the loss-of-voltage release is guaranteed to pull in, so that the circuit breaker can be closed smoothly; when the supply voltage is lower than 40% of the rated voltage, the loss-of-voltage release is guaranteed to be disconnected Make the circuit breaker trip off. Generally, the normally closed button connected in series in the electromagnetic coil circuit of the loss-of-voltage release can also be used for the opening operation.
4. Shunt release
The shunt release is used for remote-operated low-voltage circuit breaker opening control. Its electromagnetic coil is connected in parallel with the power supply side of the low-voltage circuit breaker. When the opening operation is required, press the normally open button to make the electromagnet of the shunt release get electricity to attract the armature, and push the free release mechanism through the transmission mechanism to make the low-voltage circuit breaker trip.
5. Electronic release
The electronic release can have all the above functions and can be easily adjusted. Electronic trip unit is a circuit composed of electronic components, detects the current of the main circuit, amplifies and pushes the tripping mechanism.
Thermal release protection principle
The main purpose of overheating protection is to prevent the motor from overheating. Therefore, a model to simulate the motor heating is set up in the device, and the different heating effects of positive and negative sequence overload currents are considered comprehensively, and the heating and cooling process of the motor is simulated and calculated, mainly for the heating of the motor and long-term overload. Provide protection. And it has thermal memory, that is, after the protection acts on trip or signal, the motor is allowed to start again only when the heat accumulation value is reduced to below the fixed value through the process of heat dissipation.
Thermal tripping is the tripping of the overheat protection action, and the overheating protection is the overload protection with the characteristics of delayed tripping and delayed return. Setting of thermal release: larger than the rated current (1.1 to 1.2 times).






